Circular Weaving: Traditional Art Meets Modern Innovation for Sustainable Textiles
Circular weaving, an ancient technique using specialized looms, creates continuous tubular fabrics i…….
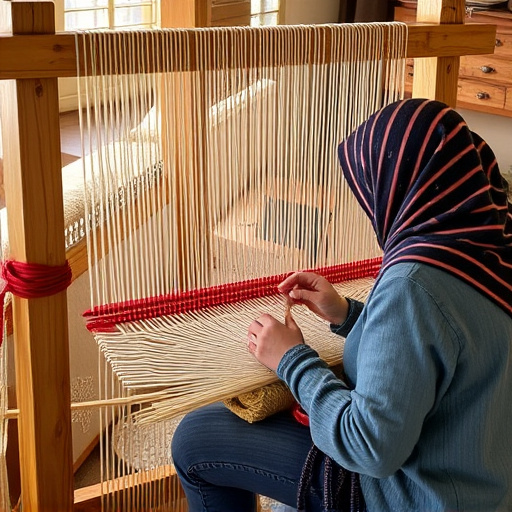

Circular weaving, an ancient technique using specialized looms, creates continuous tubular fabrics ideal for various garments. Combining traditional methods with modern machinery offers speed, precision, and sustainability. This method minimizes textile waste, reduces resource consumption, and promotes a circular economy. Using recycled materials, natural fibers, and innovative designs, circular weaving transforms fashion and design industries while preserving cultural heritage. Future trends include smart textiles and technology integration for adaptive garments and interactive art.
Discover the art of circular weaving, a unique and sustainable approach to textile creation. This ancient technique is making a modern comeback, offering an eco-friendly alternative to conventional weaving methods. From understanding its fundamentals to exploring creative applications, we delve into the world of circular weaving. Uncover traditional techniques, modern innovations, environmental advantages, and the equipment shaping this evolving craft.
- Understanding Circular Weaving: A Unique Approach
- Traditional Techniques vs. Modern Innovations
- The Environmental Impact and Benefits of Circular Weaving
- Equipment and Materials Used in the Process
- Exploring Creative Applications and Future Trends
Understanding Circular Weaving: A Unique Approach

Circular weaving, a unique approach in the art of fabric creation, involves weaving on a circular loom to produce continuous lengths of fabric, perfect for tubular shapes. Unlike traditional flat weaving methods, this technique allows for seamless construction, making it ideal for items like hats, scarves, and even clothing. Understanding circular weaving is key to unlocking the potential for innovative textile designs.
This method offers a distinct advantage by eliminating the need for seams, resulting in stronger and more durable garments. The circular motion creates a smooth, uninterrupted fabric structure, enhancing both functionality and aesthetic appeal. By embracing this ancient practice with modern twists, weavers can craft intricate patterns and textures, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible within the realm of weaving.
Traditional Techniques vs. Modern Innovations

In the realm of weaving, traditional techniques have long been the backbone of this ancient art. For centuries, craftsmen and communities around the world have perfected the skill of circular weaving, passing down knowledge from generation to generation. These timeless methods, often rooted in cultural heritage, involve manual operations such as the backstrap loom or the foot-treadle loom, allowing for intricate patterns and unique textures. The beauty of these traditional techniques lies in their simplicity and the intimate connection they foster between the weaver and the fabric.
However, with technological advancements, modern innovations have emerged, revolutionizing the weaving industry. Automated looms and advanced machinery now compete with—and sometimes surpass—traditional methods. These modern innovations offer increased speed, precision, and consistency, enabling mass production while still allowing for a degree of customization. While traditional techniques may take longer and require more skill, modern weaving technologies cater to the demands of contemporary markets, ensuring that this age-old craft remains relevant in today’s digital era.
The Environmental Impact and Benefits of Circular Weaving

Circular weaving offers a sustainable approach to traditional textile production, with significant environmental benefits. By using recycled materials and minimizing waste, this method reduces the resource-intensive nature of conventional weaving. The process involves reusing and repurposing fabrics, threads, and even discarded clothing, cutting down on the need for new raw materials and energy consumption. This not only lessens the carbon footprint associated with textile manufacturing but also contributes to a more circular economy, where resources are kept in use for longer periods.
Furthermore, circular weaving promotes a reduction in textile waste, a major environmental concern in the industry. Traditional linear production often generates vast amounts of scrap material and by-products, leading to pollution and landfill issues. Circular methods, however, aim to close this loop, ensuring that offcuts and surplus materials are given new life, thereby decreasing the overall environmental impact of weaving practices.
Equipment and Materials Used in the Process

In circular weaving, a unique and ancient technique, artisans utilize specialized equipment adapted from traditional methods. The process involves a frame constructed with a horizontal or vertical axis, often made of wood or metal, which supports a set of interwoven warps, creating a flexible base for the fabric. A shuttle, typically loaded with weft yarn, is then used to interlace through these warps, forming intricate patterns and textures.
The materials play a crucial role in this art form. Yarns, both for warps and wefts, can vary widely depending on the desired outcome. Natural fibers like wool or cotton are popular choices due to their texture and breathability. Synthetic options offer durability and color vibrancy. The loom’s design also accommodates various accessories, such as heddles, latches, and reed cards, which aid in managing the warp threads, ensuring precision and consistency throughout the weaving process.
Exploring Creative Applications and Future Trends

Circular weaving, with its ancient roots, continues to evolve and inspire creative applications in contemporary design. Weavers are experimenting with unique materials, such as recycled fabrics and natural fibers from sustainable sources, pushing the boundaries of traditional weaving techniques. This innovative approach not only offers eco-friendly alternatives but also opens up a realm of aesthetic possibilities, allowing for intricate patterns and textural explorations.
Looking ahead, future trends in circular weaving may include the integration of smart textiles, incorporating technology to create adaptive garments and interactive art installations. As digital tools become more accessible, designers can further refine their processes, ensuring minimal waste and maximizing efficiency. This sustainable practice is set to revolutionize not only fashion but also interior design, architecture, and even automotive sectors, shaping a greener and more creative future for weaving artisans worldwide.