Ethical Weaving: Sustainability, Heritage, and Consumer Choices
The history and evolution of weaving reveal its profound impact on humanity, from its early practic…….

The history and evolution of weaving reveal its profound impact on humanity, from its early practical uses to its current status as a complex craft intertwined with societal values, technological advancements, and ethical considerations. The Industrial Revolution introduced mechanical looms, revolutionizing production but also raising concerns about labor rights. Today, ethical practices in weaving are paramount, with a focus on sustainability, fair wages, and responsible sourcing of materials, reflecting a broader shift towards valuing craftsmanship, environmental stewardship, and social responsibility. Weaving's journey today emphasizes the balance between innovation and ethical production, with artisans and designers favoring sustainable materials like organic cotton, hemp, linen, and bamboo, and adhering to Fair Trade standards. The preservation of traditional weaving techniques, as a vessel for cultural heritage and storytelling, is increasingly recognized as vital, with consumers urged to support authentic, traditionally-crafted weaves to maintain the integrity of this art form. Certifications such as Fair Trade and GOTS play a crucial role in upholding ethical standards within the industry, influencing consumer purchasing decisions and promoting sustainable production methods. Ethical practices in weaving are not just about the end product but also ensuring fair treatment for artisans, thus fostering a more equitable global economy while preserving the rich tradition of weaving.
Weaving is an art that intertwines threads of creativity with those of ethical responsibility. This article explores the confluence of tradition, innovation, and morality within this craft. From historical practices to contemporary sourcing, it delves into how weaving has evolved to respect both the planet and the cultural legacies embedded in its fabric. It also examines the critical role of certifications, labels, and consumer awareness in ensuring that the weaving industry upholds ethical standards. Join us as we unravel the complex tapestry of ethics in weaving, highlighting the importance of maintaining artisanal integrity and promoting sustainable practices.
- The Historical Evolution of Ethical Practices in Weaving
- Sustainable Materials and Ethical Sourcing in Contemporary Weaving
- Artisanal Integrity: Preserving Traditional Techniques and Cultural Heritage
- The Role of Certifications and Labels in Ethical Weaving Practices
- Consumer Responsibility and Advocacy for Ethical Weaving Products
The Historical Evolution of Ethical Practices in Weaving

Throughout history, the craft of weaving has been a cornerstone of human creativity and industry, with its ethical dimensions reflecting societal values and technological advancements. Initially, the practice was rooted in necessity, with early civilizations using natural fibers such as cotton and wool to create textiles for warmth, protection, and shelter. As weaving techniques advanced, so did the ethical considerations surrounding the craft. The introduction of mechanical looms during the Industrial Revolution both revolutionized production capabilities and raised new ethical questions regarding labor practices. Artisans and workers faced challenges as machinery replaced hand-weaving, leading to debates about fair wages, safe working conditions, and the preservation of traditional weaving skills.
The evolution of ethical practices in weaving has been a response to both technological changes and social awareness. In the following centuries, movements such as the Arts and Crafts Movement championed the value of handcrafted work and the dignity of labor. This period highlighted the importance of ethical sourcing of materials and respect for the craftsmanship involved in weaving. Today, sustainability and ethical production are at the forefront of discussions within the industry. Producers and consumers alike are increasingly conscious of the environmental impact of textile manufacturing, advocating for practices that protect natural resources and ensure fair treatment of workers throughout the supply chain. Keywords: Ethical Practices in Weaving, Historical Evolution, Labor Practices, Sustainability, Craftsmanship, Handcrafted Work.
Sustainable Materials and Ethical Sourcing in Contemporary Weaving

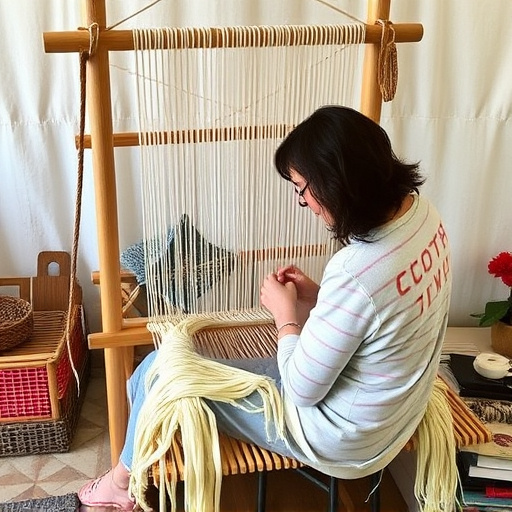
In contemporary weaving, the ethical considerations extend beyond the aesthetic and technical aspects to encompass the environmental impact and social responsibilities associated with material sourcing. Artisans and designers are increasingly conscious of the importance of utilizing sustainable materials to minimize ecological footprints. These materials include naturally grown fibers such as organic cotton, hemp, linen, and bamboo, which are not only renewable but also biodegradable. The choice of these fibers over synthetic alternatives is driven by a commitment to reduce waste and pollution typically associated with petroleum-based products. Moreover, the traceability of these materials allows weavers to ensure fair labor practices in their sourcing, promoting ethical treatment of workers throughout the supply chain. This includes adherence to Fair Trade principles that guarantee fair compensation and safe working conditions for the individuals involved in the production process. By prioritizing sustainable and ethically sourced materials, the contemporary weaving community is not only preserving traditional craftsmanship but also pioneering a more responsible approach to this ancient art form. This shift towards sustainability and ethical sourcing in weaving reflects a broader movement within the fashion and design industries, emphasizing the need for environmentally conscious and socially equitable production methods. Artisans are thus becoming stewards of both cultural heritage and environmental integrity, showcasing how weaving can serve as a powerful medium for positive change.
Artisanal Integrity: Preserving Traditional Techniques and Cultural Heritage

Artisanal integrity in weaving is a multifaceted issue that encompasses the preservation of traditional techniques and respect for cultural heritage. The intricate craft of weaving, a practice as old as civilization itself, holds within it the stories, values, and histories of communities around the globe. As globalization and industrial advancements present new challenges to these artisanal practices, it becomes imperative to safeguard the unique techniques that have been passed down through generations. Each weave tells a tale of ancestral wisdom, local materials, and regional styles, contributing to a rich tapestry of human creativity. In this context, ethical considerations extend beyond the mere act of weaving; they involve honoring the origins and contexts from which these techniques emerged. By supporting artisans who adhere to traditional methods, consumers can play a role in maintaining the integrity of this craft and ensuring that cultural heritage is not lost to the march of time or the pull of modernity. It is through conscious consumption and appreciation for the craftsmanship involved in weaving that these traditions are kept alive, allowing them to continue influencing and inspiring new generations of artisans.
The Role of Certifications and Labels in Ethical Weaving Practices

In the realm of ethical textile production, certifications and labels play a pivotal role in ensuring responsible practices within the weaving industry. These certifications often adhere to rigorous standards set by reputable organizations that assess labor conditions, environmental impact, and material sourcing. For instance, certifications like Fair Trade and Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) provide consumers with assurance that the weaving processes are carried out under fair labor practices and with environmentally sustainable materials. These labels not only guide consumer choices but also incentivize manufacturers to adhere to ethical standards, thereby promoting a more equitable and sustainable industry. As such, they serve as a marker of integrity, allowing artisans to showcase their commitment to ethical weaving, which can enhance brand reputation and customer trust.
The proliferation of certifications and labels has also led to increased transparency and accountability within the supply chain. Consumers are becoming more discerning, often seeking products that align with their values of social responsibility and environmental stewardship. By engaging with certified weaving practices, brands can demonstrate due diligence and a responsible approach to their production processes. This not only fosters consumer loyalty but also encourages a broader shift towards ethical manufacturing, ultimately influencing the industry’s trajectory towards more sustainable and fair practices. The integration of these certifications and labels into the weaving process is thus not merely a marketing tool but a cornerstone for building a responsible and future-proof industry.
Consumer Responsibility and Advocacy for Ethical Weaving Products
Ethical considerations in the realm of weaving extend beyond the aesthetic and functional aspects of the craft, encompassing the social responsibility of both producers and consumers. As consumers engage with weaving products, they play a pivotal role in advocating for ethical practices within the industry. By choosing to support artisans who use sustainable materials and fair labor practices, consumers can drive positive change. These choices not only preserve traditional weaving techniques but also ensure that the weavers receive equitable compensation, thereby promoting their well-being and the longevity of their craft.
Advocacy for ethical weaving products is a multifaceted endeavor that involves transparency from suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers. It encompasses the responsible sourcing of materials, fair wages for artisans, and safe working conditions. Consumers who prioritize ethically made weaving items contribute to a more just global economy. They encourage businesses to adopt practices that respect both people and the planet. This consumer-driven advocacy can lead to industry-wide improvements, ensuring that the legacy of weaving traditions continues to thrive in an ethical manner.









