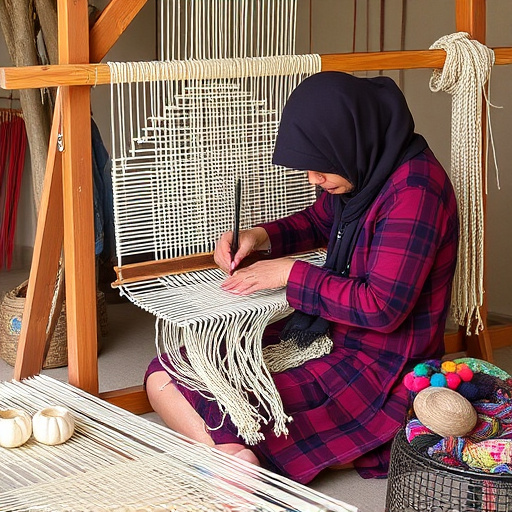
Ethical Weaving: Sustainability, Tradition, and Responsibility in Modern Craft
The evolution of weaving from ancient times to modern days reflects a continuous adaptation to soci…….
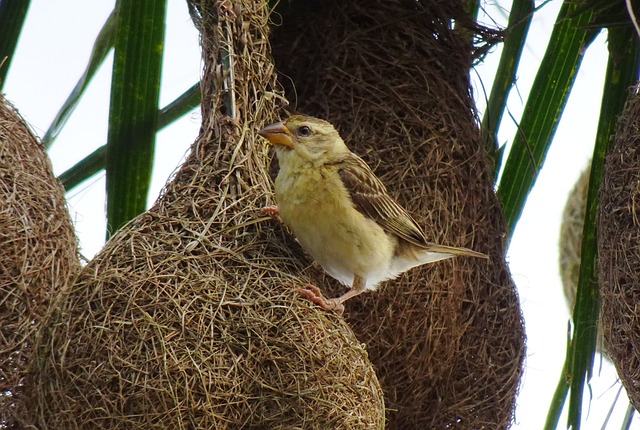

The evolution of weaving from ancient times to modern days reflects a continuous adaptation to societal values and ethical standards. Historically, it has been a barometer for ethical practices, reflecting the shifts in who engages in the craft and the ethical challenges faced during the Renaissance and Industrial Revolution. Today, the weaving industry stands at a juncture where sustainability and ethics are paramount, driven by consumer demand for environmentally responsible and socially equitable products. Brands are increasingly adopting sustainable materials like organic and recycled fibers to minimize environmental impact, while also ensuring fair labor practices and safe working conditions. This transformation underscores the importance of maintaining traditional weaving techniques and cultural heritage, as well as the need for ethical sourcing of both natural and synthetic fibers to protect ecosystems and promote the well-being of artisans. Consumer choices are now a powerful force in shaping the industry's trajectory towards greater sustainability, ethical production, and quality. The article highlights the critical role of informed consumer decisions in fostering a more responsible and equitable weaving industry.
Weaving, an art as old as civilization, intertwines history with ethics. This article explores the historical context of ethical considerations in weaving, from ancient practices to contemporary challenges. It delves into the importance of sustainability and ethical sourcing within modern industries, emphasizing the role of consumers in shaping responsible market demands. Additionally, it highlights the significance of preserving cultural integrity through artisanal craftsmanship and the use of natural and synthetic fibers that honor both tradition and environment. Join us as we unravel the threads of ethics in the tapestry of weaving.
- The Evolution of Weaving Ethics: A Historical Perspective
- Sustainability and Ethical Practices in Modern Weaving Industries
- Cultural Integrity and Responsible Artisanship: Preserving Traditional Techniques
- Material Considerations: Ethical Sourcing of Natural and Synthetic Fibers
- The Role of Consumers in Ethical Weaving Practices and Market Demands
The Evolution of Weaving Ethics: A Historical Perspective

Throughout history, the practice of weaving has been integral to human civilization, serving not just as a craft but also as an expression of cultural values and ethical considerations. The earliest woven textiles are believed to date back to the Neolithic period, with evidence found in regions across the world from Central America to Asia. As weaving techniques evolved, so did the ethical dimensions inherent in this craft. In ancient civilizations like those of Egypt, Greece, and Rome, weaving was often associated with specific social roles and gender expectations. The ethical considerations of the time were reflected in who was allowed to weave and what they were permitted to create.
The Middle Ages saw a shift where monasteries and convents became centers for textile production, governed by religious principles that emphasized stewardship and communal responsibility. This period highlighted the ethical implications of resource management and fair labor practices. As trade routes expanded during the Renaissance and into the Industrial Revolution, weaving evolved from a local craft to an industrial enterprise. With this shift came new ethical challenges, including the treatment of workers, child labor, and the environmental impact of mass production. The history of weaving ethics is thus a reflection of broader societal values, highlighting how ethical considerations have been woven into the very fabric of this practice over time, from artisanal creation to mechanized production, underscoring the importance of ongoing dialogue and action to ensure ethical practices in the weaving industry.
Sustainability and Ethical Practices in Modern Weaving Industries

Within the modern weaving industry, sustainability and ethical practices have become paramount in addressing the environmental and social impacts associated with textile production. The process of weaving, traditionally a craft that has intertwined human ingenuity with natural fibers, now faces the challenge of balancing technological advancements with eco-conscious materials and methods. As consumers increasingly demand transparency and responsibility from brands, the weaving sector is adapting to incorporate sustainable initiatives. This includes the use of organic and recycled fibers that reduce the carbon footprint, conserve water resources, and decrease waste production. Moreover, ethical practices ensure fair labor conditions, safe working environments, and equitable treatment for artisans and workers involved in weaving processes worldwide. These efforts not only contribute to the well-being of communities but also foster a reputation for integrity and durability in the products they create, thereby aligning the industry with the values of an environmentally and socially conscious clientele. The integration of sustainable and ethical practices is a testament to the adaptability of weaving as an art form and its potential to positively impact both the planet and the people it touches.
Cultural Integrity and Responsible Artisanship: Preserving Traditional Techniques

The art of weaving is deeply interwoven with cultural identities, carrying narratives that are as varied as the techniques themselves. As global markets and consumer trends increasingly influence craft traditions, it becomes imperative to uphold the integrity of these practices. Artisans play a pivotal role in this endeavor, serving as custodians who pass down weaving skills through generations. To preserve traditional techniques, responsible artisanship demands a commitment to authenticity and quality over mass-production. By embracing sustainable methods and valuing the origins of their craft, weavers can ensure that the cultural significance of each pattern and textile remains vibrant and respected. This not only maintains the historical continuity of the craft but also supports local economies and empowers communities. In an age where globalization threatens to homogenize cultural expressions, it is the dedication of these artisans to their traditional weaving techniques that keeps alive the diverse tapestry of human creativity. Engaging with fair trade practices and promoting education in weaving techniques are steps that can be taken to support this noble pursuit, ensuring that the rich heritage of weaving is honored and its future secured for generations to come.
Material Considerations: Ethical Sourcing of Natural and Synthetic Fibers

Ethical considerations are paramount in the realm of weaving, particularly concerning the sourcing of both natural and synthetic fibers. The ethical procurement of these materials ensures that the production process aligns with environmental sustainability and social responsibility. Natural fibers such as cotton, wool, and silk require careful consideration to ensure they are harvested without causing harm to ecosystems or exploiting labor. For instance, organic cotton farming practices protect soil health and conserve water while providing fair wages and working conditions for farmers. Similarly, the sourcing of synthetic fibers should consider the environmental impact of their production, which often involves petroleum-based chemicals. Opting for recycled or biodegradable alternatives can mitigate the ecological footprint associated with these materials. Companies that prioritize ethical sourcing are typically transparent about their supply chains, allowing consumers to make informed decisions and supporting industries that respect both people and the planet in the weaving process.
In addition to the origin of the fibers, the ethical implications of weaving extend to the labor practices involved in transforming these materials into textiles. It is crucial to support artisans and weavers who operate under fair labor conditions, ensuring that their craft contributes positively to their livelihoods rather than perpetuating cycles of poverty or exploitation. By choosing suppliers that adhere to ethical standards, consumers can indirectly promote sustainable practices and contribute to the well-being of communities involved in the intricate art of weaving. The selection of ethically sourced fibers is a testament to a commitment to responsible consumption and a step towards a more equitable and sustainable future for this traditional craft.
The Role of Consumers in Ethical Weaving Practices and Market Demands

The intricate process of weaving is not solely an artisanal craft but also a complex industry that intertwines with ethical considerations. Consumers play a pivotal role in shaping the ethical landscape of weaving by influencing market demands through their purchasing decisions. As conscious consumers become more informed about the origins and production methods behind textiles, there is a growing preference for ethically produced goods. This shift in consumer behavior has led to increased demand for sustainably sourced materials, fair labor practices, and environmentally friendly weaving techniques.
Moreover, the purchasing power of consumers can drive manufacturers and retailers to adopt more responsible practices. By favoring brands that uphold ethical standards over those that do not, consumers can encourage transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain. This consumer-driven push for integrity in the weaving industry ensures that businesses prioritize the well-being of workers, the health of the environment, and the quality of the products they offer. Through their choices, consumers have the power to promote a culture of ethical responsibility within the realm of weaving, ultimately fostering a more sustainable and equitable marketplace.