Reviving Tradition: The Role of Weaving in Slow Fashion’s Sustainable Future
The slow fashion movement integrates traditional weaving techniques with modern sustainability prac…….

The slow fashion movement integrates traditional weaving techniques with modern sustainability practices, emphasizing cultural preservation and ethical production as alternatives to fast fashion's disposable culture. This approach celebrates the art of weaving, highlighting the unique patterns, textures, and narratives that come from handcrafted methods, which in turn honor both cultural heritage and environmental stewardship. Artisans worldwide, including those from Peru and Japan, maintain these practices, not only as a part of their cultural identity but also as a means to provide sustainable livelihoods. The movement values the craftsmanship and cultural diversity that weaving embodies, which in turn enriches communities economically and promotes environmental sustainability. Weaving's role in slow fashion is crucial, serving as a narrative of cultural heritage, social equity, and ecological responsibility, and aligning with consumer preferences for sustainable textiles. This synergy between tradition and modernity within the weaving community exemplifies the resilience and creativity of artisans, fostering knowledge exchange and sustainable practices that are central to slow fashion's ethos. The movement champions a model that prioritizes quality, respect for tradition, and ethical practices, making it a more thoughtful and meaningful approach to apparel within the global fashion industry.
Handwoven textiles have long been intertwined with human history, serving as both functional and artistic expressions. Today, weaving stands at the heart of slow fashion, a movement that champions sustainable practices, cultural heritage, and artisanal craftsmanship over mass production. This article explores the resurgence of traditional weaving techniques and their pivotal role in promoting eco-friendly materials and ethical consumption. From preserving ancient crafts to innovating with modern technology, we will delve into how weaving sustains cultural identities, supports local economies, and invites consumers to make mindful fashion choices. Join us as we unravel the intricate tapestry of slow fashion weaving and its global impact.
- The Artisanal Resurgence: Weaving's Role in Slow Fashion
- Heritage Techniques: Preserving Ancient Weaving Crafts
- Sustainable Yarns: Eco-Friendly Materials in Modern Weaving
- Community and Cooperation: Weavers as Artisans and Innovators
- The Slowing Down Movement: A Philosophy for Consumers and Creators Alike
The Artisanal Resurgence: Weaving's Role in Slow Fashion

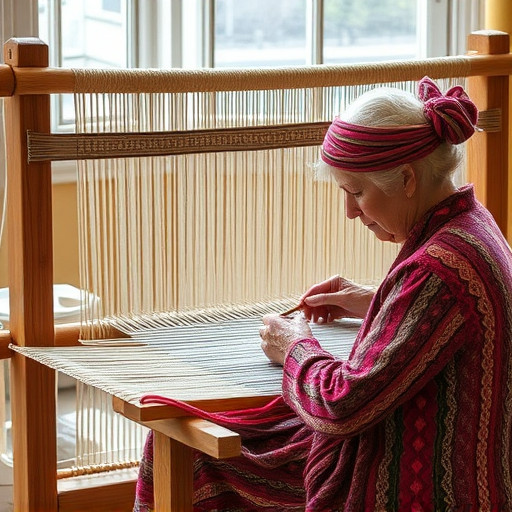
Weaving plays a pivotal role in the slow fashion movement, representing a harmonious blend of tradition and sustainability. The resurgence of artisanal weaving techniques not only celebrates the craftsmanship of weavers around the world but also contributes to a more responsible approach to textile production. This revival is a testament to the enduring relevance of these age-old practices, as they offer an alternative to fast fashion’s disposable culture. In slow fashion, there is a conscious effort to honor the skills involved in weaving by showcasing the intricate patterns and textures that only patient, handcrafted processes can yield. The result is a garment or fabric with a story, one that respects both the environment and the artisan’s time-honored methods. This narrative stands in stark contrast to mass-produced items, which often overlook the human element and environmental impact of their creation. By championing weaving within slow fashion, there is a renewed focus on the tangible connection between wearers and creators, fostering a deeper appreciation for the garments’ origins and the cultural heritage they represent.
Heritage Techniques: Preserving Ancient Weaving Crafts

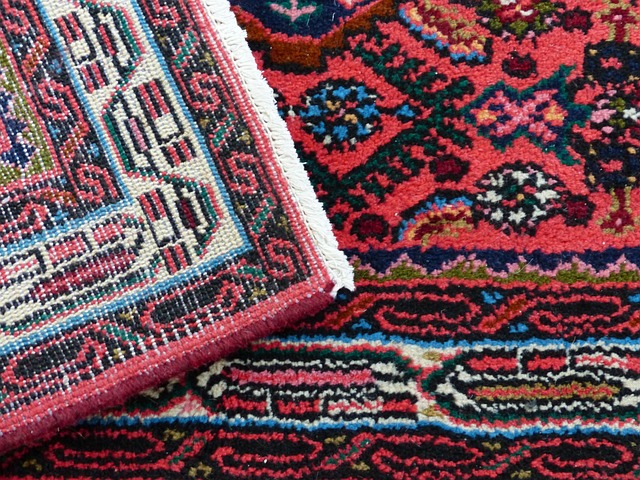
The practice of weaving serves as a vital thread connecting the past with the present within the slow fashion movement. Heritage techniques in weaving are a testament to humanity’s enduring relationship with textiles, representing a legacy passed down through generations. These ancient crafts involve intricate patterns, labor-intensive processes, and unique materials that are deeply rooted in cultural identities. Artisans around the world, from Peru to Japan, continue to practice these traditional weaving methods, which not only sustain a rich tapestry of history but also offer a sustainable alternative to fast fashion. By preserving these techniques, these artisans ensure the survival of their cultural heritage while contributing to a more conscious and responsible approach to clothing production. This preservation is not merely an act of nostalgia; it is an essential practice that fosters economic empowerment and environmental sustainability within communities. The slow fashion movement champions these weaving traditions, highlighting the importance of craftsmanship, cultural diversity, and the ethical treatment of artisans. Through this lens, weaving becomes more than a mere craft; it is a narrative of cultural continuity, social equity, and planetary stewardship.
Sustainable Yarns: Eco-Friendly Materials in Modern Weaving

In recent years, the weaving craft has been reimagined within the context of slow fashion, where sustainability and eco-consciousness take center stage. Artisans and designers are increasingly turning to sustainable yarns, which are not only kind to the planet but also align with the ethos of slow fashion. These yarns are derived from a variety of natural sources, including organic cotton, hemp, linen, and even recycled materials. The choice of these fibers over their conventional counterparts is pivotal in reducing the environmental impact associated with textile production. For instance, organic cotton requires less water to grow and doesn’t depend on harmful pesticides, making it a more sustainable option. Hemp, known for its durability and versatility, is another eco-friendly material that offers breathability and strength. These fibers are spun into yarns that become the foundation of slow fashion garments and accessories, each piece telling a story of environmental stewardship and ethical production. The weaving process itself, whether done by hand or with modern machinery, becomes a testament to the blend of tradition and innovation in sustainable textile creation. As consumers become more aware of their purchasing power and the environmental consequences of fast fashion, the demand for garments made with eco-friendly yarns continues to rise, driving the industry towards a more sustainable future through the art of weaving.
Community and Cooperation: Weavers as Artisans and Innovators
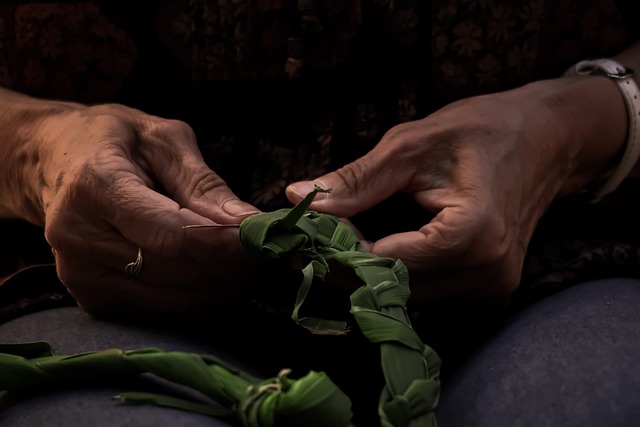

In the realm of slow fashion, weaving emerges as a practice that not only preserves traditional craftsmanship but also fosters community and cooperation among artisans. Weavers, often seen as custodians of ancestral techniques, collaborate to innovate and adapt their craft to contemporary needs without sacrificing the integrity of their cultural heritage. This interplay between heritage and modernity is a testament to the resilience and creativity inherent in the weaving community. The synergy within these communities allows for knowledge exchange, where each weaver contributes unique skills, ensuring the collective evolution of their craft. This collaborative approach not only enriches individual skill sets but also leads to sustainable practices that align with slow fashion’s ethos of respecting both people and the planet.
The interconnectedness of artisans in the slow fashion movement is a powerful driver for positive social and economic change. Weavers across different regions share patterns, techniques, and designs, creating a tapestry of shared knowledge that transcends geographical boundaries. This communal spirit also extends to supporting local economies and providing sustainable livelihoods. The commitment to weaving as an art form within the slow fashion framework underscores the importance of valuing the labor, time, and cultural significance behind each handcrafted piece. Through this collaborative network, weavers become innovators, continually redefining what it means to be a part of the global fashion industry while maintaining their unique identities and traditions.
The Slowing Down Movement: A Philosophy for Consumers and Creators Alike
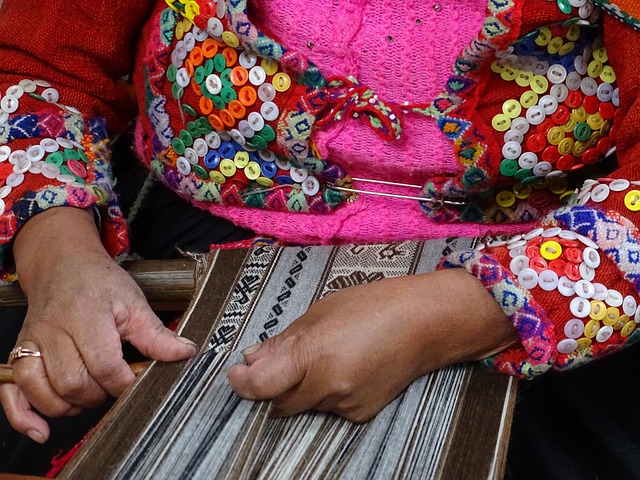

The resurgence of traditional weaving practices is a testament to their enduring significance in the context of slow fashion. This movement, which advocates for mindful consumption and sustainable production, finds a natural ally in the craft of weaving. Artisans around the globe invest countless hours perfecting this skill, ensuring each piece is imbued with intention and care. The result is a product that stands in stark contrast to the fast-paced, disposable nature of fast fashion. By emphasizing handcrafted techniques like weaving, slow fashion underscores the value of labor and the stories embedded within each textile. Consumers are encouraged to appreciate garments not just for their aesthetic or function but also for the cultural heritage and environmental sustainability they represent. This philosophy fosters a deeper connection between wearer and worn, as the intricate patterns and unique qualities of hand-woven fabrics become more than mere clothing—they evolve into wearable art with a narrative that spans generations. In this way, weaving becomes a tangible expression of the slow fashion ethos, championing a model where quality, respect for craftsmanship, and ethical production are paramount.