Sustainable Weaving Revolution: Eco-Friendly Yarns and Circular Designs for a Greener Future
The article delves into the transformation of weaving practices from their historical roots to cont…….

The article delves into the transformation of weaving practices from their historical roots to contemporary sustainable methods. It emphasizes how early civilizations used natural materials sustainably, and as weaving evolved with the industrial revolution, environmental impacts grew, prompting a shift back to eco-friendly practices. Current sustainable weaving practices utilize biodegradable materials, low-impact dyes, and energy-efficient techniques to minimize waste and environmental footprints. Innovations like organic or recycled fibers, local sourcing of materials, and the use of reclaimed yarns are critical in this green evolution. The adoption of natural dyes from plants and insects, along with renewable energy sources in loom operations, showcases the commitment to sustainability within the weaving industry. Additionally, zero-waste design methodologies and digital technology advancements further reduce waste and resource consumption, ensuring that weaving remains a relevant, sustainable craft that aligns with modern environmental and economic objectives. Consumer preference for eco-conscious textiles is driving artisans to innovate, ensuring the preservation of traditional weaving skills while also addressing contemporary environmental concerns. This evolution highlights how sustainable consumer choices can support and sustain the weaving industry, guaranteeing its longevity and ethical integrity.
Exploring the interplay of tradition and innovation, “Sustainability in Weaving” delves into the evolving landscape of textile production. This article traverses the historical thread of sustainable practices, from their origins to contemporary advancements, emphasizing the significance of material selection and energy conservation in the weaving process. It highlights groundbreaking zero-waste weaving designs that minimize environmental impact, and underscores the critical roles of both consumers and artisans in championing these practices on a global scale. Join us as we unravel the narrative of sustainability within the fiber arts, ensuring a resilient and environmentally conscious future for weaving.
- The Evolution of Sustainable Weaving Practices: A Historical Perspective
- Material Matters: Choosing Eco-Friendly Yarns for Contemporary Weaving
- Energy Efficiency in the Loom: Innovative Techniques for Sustainable Production
- Waste Not, Weave Much: Zero-Waste Approaches in Modern Weaving Designs
- The Role of Consumers and Artisans in Promoting Sustainable Weaving Practices Globally
The Evolution of Sustainable Weaving Practices: A Historical Perspective

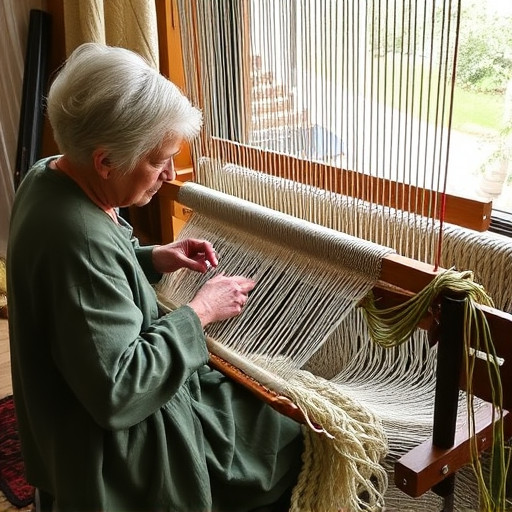
The practice of weaving has a long and storied history, intertwined with humanity’s quest for textiles that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. From the earliest looms crafted by ancient civilizations to the sophisticated mechanical looms of today, the evolution of sustainable weaving practices reflects a continuous adaptation to environmental constraints and ethical considerations. Ancient cultures demonstrated a form of sustainability through their careful selection of natural fibers and dyes, often derived from local flora and fauna, which minimized ecological impact and aligned with available resources. As centuries passed, the industrial revolution brought significant changes, including mass production that sometimes came at the cost of the environment. However, awareness of the detrimental effects of unsustainable practices led to a resurgence of eco-conscious weaving methods. Innovators began integrating biodegradable materials and low-impact dyes, while also optimizing energy consumption and waste reduction in the weaving process. This shift towards sustainability is not merely a response to contemporary environmental challenges but a return to the principles that governed early weaving practices, albeit with modern knowledge and technology. Today, sustainable weaving encompasses everything from the ethical sourcing of raw materials to the implementation of closed-loop systems that minimize water usage and effluents, ensuring that the tradition of weaving continues to thrive while respecting and preserving our planet’s resources for future generations. The journey towards sustainable weaving is ongoing, with each step forward informed by a deep appreciation for both the art of weaving and the natural world it depends on.
Material Matters: Choosing Eco-Friendly Yarns for Contemporary Weaving

In recent years, the practice of weaving has seen a significant shift towards sustainability, with artisans and designers increasingly opting for eco-friendly yarns. The choice of materials in weaving is pivotal, as it directly impacts the environmental footprint of the final textile product. Opting for organic or recycled fibers not only reduces the strain on natural resources but also lessens the carbon footprint associated with production. For instance, the use of locally sourced wool or cotton minimizes transportation emissions, while also supporting local economies. Additionally, the integration of reclaimed yarns salvaged from post-consumer waste streams can significantly lower the demand for virgin materials and contribute to a circular economy within the weaving industry. These eco-conscious choices in yarn selection ensure that the act of weaving becomes an integral part of the broader sustainable fashion movement, emphasizing the importance of material matter in contemporary weaving practices.
The transition towards sustainability in weaving is not merely about using less harmful materials; it’s also about embracing innovative techniques and technologies. For example, natural dyes extracted from plants or insects offer a safer alternative to synthetic dyes, which often contain toxic chemicals. Similarly, the development of biodegradable yarns that break down naturally at the end of their life cycle is a game-changer in the industry. These advancements underscore the commitment of weavers to environmental stewardship and highlight the potential for weaving to lead the way in sustainable textile production. By prioritizing eco-friendly yarns and processes, weaving becomes not just a craft but a powerful tool for promoting sustainability in the textile industry at large.
Energy Efficiency in the Loom: Innovative Techniques for Sustainable Production

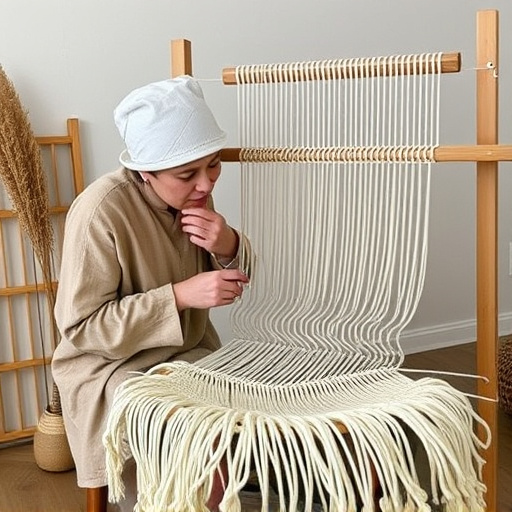
In the realm of sustainable production, the integration of energy efficiency in the loom is paramount for weaving to remain a viable and eco-conscious craft. Modern weaving operations consume significant amounts of energy, primarily from electricity used to power looms. To mitigate this impact, innovators are exploring renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power to drive these machines. By transitioning to green energy, the carbon footprint associated with traditional weaving can be drastically reduced. Moreover, advancements in loom technology have led to the development of energy-efficient models that optimize energy consumption through improved design and intelligent control systems. These systems not only save energy but also enhance the precision and speed of the weaving process, leading to less waste and more consistent product quality. The adoption of these technologies not only ensures the longevity of the craft but also aligns it with the global sustainability goals, positioning weaving as a forward-thinking industry that values both resource conservation and high-quality output. As such, the integration of energy efficiency in the loom is a critical step towards making weaving practices more sustainable, ensuring that this tradition continues to thrive in an environmentally conscious world.
Waste Not, Weave Much: Zero-Waste Approaches in Modern Weaving Designs

Modern weaving practices have evolved significantly, incorporating sustainable methods that prioritize resource efficiency and minimal waste. The ‘Waste Not, Weave Much’ philosophy is a testament to the innovative approaches in the industry, emphasizing the circular economy principles within textile production. Designers and manufacturers are now integrating zero-waste design strategies, which involve carefully planning patterns to use every fiber possible, thus reducing leftover materials that would otherwise contribute to landfills. This approach requires a deep understanding of material properties and creative pattern design that allows for the optimal utilization of yarns without excess. By adopting these methods, the textile industry not only promotes sustainability but also fosters economic growth by adding value to every thread, ensuring that weaving processes align with environmental conservation efforts. The integration of digital technology, such as advanced software that simulates material usage before physical production begins, further enhances the precision and efficiency of zero-waste weaving designs, leading to a significant reduction in waste across the industry. This shift towards a more sustainable future in weaving is not only commendable but also demonstrates the adaptability and innovation within the field, setting a new standard for responsible textile production.
The Role of Consumers and Artisans in Promoting Sustainable Weaving Practices Globally

The intricate craft of weaving, a practice steeped in history and cultural significance, is at a pivotal crossroads as it confronts the imperative for sustainability. Consumers play a crucial role in this shift by making informed choices that favor sustainable practices. By valuing and purchasing eco-friendly materials and ethically produced textiles, consumers incentivize weavers to adopt sustainable methods, thereby preserving both the environment and the art of weaving itself. This demand for responsible products influences artisans to reduce their ecological footprint, whether by sourcing organic or recycled fibers, employing less polluting dyeing techniques, or optimizing energy usage in their workshops. Artisans who embrace these practices not only contribute to the health of our planet but also ensure the longevity and integrity of their craft. The synergy between consumer awareness and artisan innovation is essential for nurturing a global culture of sustainability within the weaving industry, ultimately safeguarding this vital art form for future generations. It is through this symbiotic relationship that sustainable weaving practices can flourish, offering a model for other craft sectors to follow.